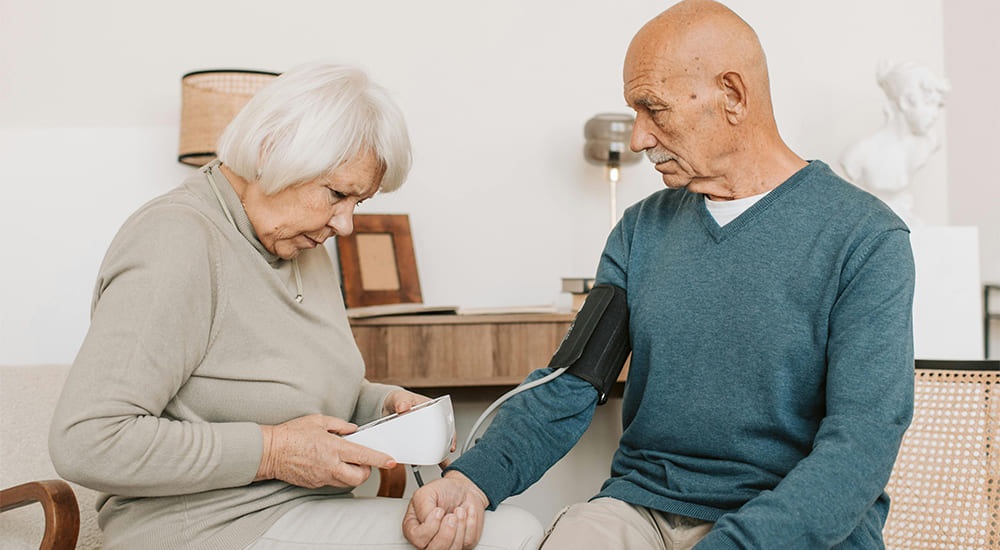
Caregivers need to understand the reasons why dementia patients are resistant to showers in order to provide more effective and compassionate care during bath time. Factors that contribute to these reluctances include sensory overload, loss of control, and the fear of discomfort. Exploring these various reasons and implementing practical solutions tailored to the individual patient can help caregivers create a bathing ritual that promotes ease and comfort for the patient’s well-being. By addressing the primary reasons behind the resistance and presenting various tried and true techniques, caregivers can choose methods that foster positive bathing habits.

Christopher Ravn
Key Takeaways
1. Dementia patients may resist showers due to factors such as sensory overload, loss of control, and past negative experiences, stemming from cognitive impairments and emotional responses.
2. Fear and discomfort during showers often result from sensory overload and feelings of vulnerability. Caregivers can alleviate these concerns by creating a comfortable and safe environment, establishing routines, and approaching showering with empathy and patience.
3. Adapting showering practices to accommodate physical limitations, past positive experiences, and the stage of dementia is essential for promoting comfort, autonomy, and hygiene maintenance in dementia patients. Caregivers should receive training to understand the unique hygiene needs and challenges associated with dementia care.
Table of Contents
1. Why Won't Dementia Patients Take Showers?
2. What Causes Discomfort Or Fear Of Showers In Dementia Patients?
3. How To Get Someone With Dementia To Shower
4. What Do You Do When A Dementia Patient Refuses To Shower?
5. How Often Should Dementia Patients Shower?
6. Dementia And Alzheimer's Shower Refusal
7. What Stage Of Dementia Affects Bathing Habits?
8. General Concerns And Inquiries About Showering
9. Frequently Asked Questions About 'why Won't Dementia Patients Take Showers
Why Won't Dementia Patients Take Showers?
To understand why patients with dementia resist showering, one must grasp the nature of the disease itself and how it affects daily activities like personal hygiene. Dementia causes damage to cognitive functions, impairing reasoning, memory, and communication, resulting in individuals who struggle to comprehend the need for personal care such as showering.
The most common reasons for resistance to showering in patients with dementia include fear, confusion, and past experiences. The fear of water, slipping, or unfamiliar environments can provoke anxiety and resistance when the need to shower arises. Additionally, confusion about why they need to shower or forgetfulness about the process involved can lead to avoidance behavior. Past negative experiences, coupled with feelings of embarrassment or discomfort during previous shower attempts, may also contribute to resistance at bath time.
With a newfound recognition and understanding of these reasons, caregivers can approach shower time with patience and empathy, helping patients alleviate their concerns and addressing their needs to create more enjoyable bath experiences.
What Causes Discomfort Or Fear Of Showers In Dementia Patients?
The fear and discomfort experienced by dementia patients during showers stem from various factors, including the loss of independence and control, as well as sensory overload.
Individuals with dementia can feel overwhelmed during showers due to sensory overload. The various sensations caused by the noise of running water, the sensation of water pressure, and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations may trigger distress or anxiety, leading to resistance to showers.
Feelings of discomfort and fear are common in those who experience loss of control and independence. Dementia often leads to a loss of autonomy, forcing patients to depend on others for help with personal care tasks like showering. The feeling of vulnerability and embarrassment provoked by this loss of control leads to avoidance of showers as patients cringe at the thought of being assisted with such a privately intimate task. Thus, sometimes one needs to understand how to deal with fixation in dementia in this situation.
It’s crucial for caregivers to understand these underlying factors and adapt their approach to showering with empathy and sensitivity. Deploying strategies to reduce discomfort and fears while creating a more positive bathing experience is essential for the well-being of the patient.
How To Get Someone With Dementia To Shower
Encouraging a person with dementia to shower voluntarily is a daunting challenge, but caregivers employ various strategies to facilitate and promote better bathing experiences. It is also important to select gifts for dementia patients that will help them remember happy moments and gets their mind off the challenge.
Firstly, it’s essential to create a comfortable and safe environment. This involves implementing fall prevention measures such as installing grab bars and non-slip mats, minimizing noise and distractions, and ensuring the water temperature is comfortable.
Additionally, making the bathroom more inviting with familiar elements like soft towels, pleasant scents, and soothing music can help alleviate anxieties and promote relaxation.
Establishing a routine is equally important. Routines provide predictability and consistency, which can help reduce resistance to showering by creating a sense of familiarity and structure. Setting a regular shower schedule and following the same steps each time can make the process less intimidating for the dementia patient and more manageable for everyone involved.
Approaching showering with empathy and patience is crucial. Caregivers should adopt a strategic approach that encourages good hygiene while respecting the patient’s autonomy and dignity. By understanding and addressing the individual’s needs and concerns, caregivers can make showering a more comfortable and positive experience for dementia patients.
What Do You Do When A Dementia Patient Refuses To Shower?
Effective communication techniques are crucial when dealing with resistant patients at shower time. Approaching the situation with empathy and patience, using clear and simple language to explain the necessity of bathing, while respecting the individual’s autonomy and dignity, can create a sense of reassurance and validation, reducing resistance and anxiety.
Employing alternative options such as sponge baths or no-rinse products may also prove helpful when showering is not feasible. These methods are seen as gentler and less overwhelming for individuals with dementia, providing a more welcomed and convenient means to maintain good personal hygiene without the challenges associated with traditional showers.
Caregivers can further reduce resistance to showering by employing effective communication techniques and offering alternative methods. By acknowledging and validating the patient’s feelings with compassion and flexibility, caregivers can help preserve their dignity and comfort during the bathing process.
We Believe Prioritizing Brain Health Enhances Your Quality Of Life
Get to know our team, our mission and how our EVY LIGHT® can provide you and your loved ones with a fuller life, letting you breathe a little easier.
How Often Should Dementia Patients Shower?
Balancing hygiene maintenance with the preferences and comfort of dementia patients is crucial when determining shower frequencies. While regular baths are essential for overall cleanliness and skin health, the frequency of bathing should be tailored to individual circumstances, such as mobility limitations, skin sensitivity, and personal preferences. Caregivers must communicate with their patients to understand their hygiene needs and formulate shower schedules and methods that address both physical and emotional needs.
Flexibility in hygiene routines becomes increasingly important as dementia progresses. Being able to adapt expectations and embrace different methods, such as using no-rinse products or sponge baths, facilitates accommodation to the evolving preferences and capabilities of the patient while still upholding proper hygiene practices. By adjusting the hygiene routine to suit individual needs, caregivers demonstrate to the patient that their dignity and comfort are valued, thereby easing the caregiver’s role in ensuring their health and cleanliness.
Adapting Bathing And Showering Practices To Physical Needs
Adapting showering and bathing routines to accommodate the physical needs of dementia patients is essential for ensuring their comfort and safety. Practical modifications to the bath and shower environment, such as addressing trip and fall hazards, installing grab bars, using shower chairs for added safety and support, pre-adjusting water temperature to prevent scalding, and providing adequate lighting, are effective safety enhancement measures.
Ergonomic aids like handheld showerheads and long-handled sponges can further improve the bathing experience, making it less strenuous for both caregiver and patient. By implementing ergonomic aids and other safety measures, caregivers create an optimal environment that promotes the personal independence of the patient while reducing the risk of injuries and enhancing the overall patient experience.
Dementia And Alzheimer's Shower Refusal
Understanding why Alzheimer’s and dementia patients refuse to shower is crucial for managing bathtime effectively. Identifying behavioral triggers such as fear, discomfort, and confusion helps caregivers address the underlying issues to reduce resistance. Strategies for managing refusal involve empowering patients with choices, gentle redirection, and avoiding conflicts by knowing when to be firm or flexible.
In responding to shower refusal, empathy and flexibility are key, as forcing patients against their will can cause distress and increase resistance. Instead, proactive approaches that consider the patient’s preferences and needs lead to a more positive and easier bathtime experience. Navigating with compassion and respect for the challenges faced by Alzheimer’s and dementia patients is essential.

Recognizing Physical Limitations In People With Dementia
There are common physical challenges faced by dementia patients that significantly impact their ability to shower independently. These challenges include muscle weakness, mobility issues, imbalance, and coordination difficulties. Additionally, vision and hearing impairments make showering an even more daunting task.
To effectively address these limitations, it’s crucial for caregivers to understand the extent of support needed by individuals with dementia. This may involve assisting with observed physical limitations or addressing behavioral issues during activities like bathing by making necessary adjustments when signs of difficulty or discomfort arise.
Seeking advice from geriatric or occupational therapists and other healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights and suggestions for creating a better bathing experience tailored to the unique needs of each individual. Further assessments of the environment may be necessary to identify additional modifications or suggestions that caregivers may not have considered. Through guidance and tips on physical actions or assistive devices, caregivers can reduce the risk of injury and maintain the independence and dignity of patients while ensuring their safety and well-being during showering.
Reconnecting With Past Positive Experiences
Repeating past positive experiences can help make showering more welcoming for patients with dementia. Caregivers should encourage positive reminiscing with patients by incorporating familiar elements from the past into the current shower routine. These elements may include favorite songs or music from their younger years, displaying cherished photographs, or using toiletries and scents that evoke pleasant memories.
Positive associations can also be created by linking storytelling to healthy hygiene habits. Engaging the individual in discussions about past experiences related to positive or interesting bathing stories can evoke warm and comforting feelings. Additionally, incorporating memory aids such as visual schedules or step-by-step guides can reassure the patient of the safety and structure of the past experience, fostering confidence and empowerment.
Leveraging positive past experiences can help transform the shower routine into a more enjoyable and meaningful activity for patients with dementia.

Enhance your brain performance through the power of light.
Comfortable and easy to use 40Hz light therapy to support and improve your brain function.
View Our LightWhat Stage Of Dementia Affects Bathing Habits?
The impact of dementia varies depending on the stage of the disease, particularly in relation to bathing. In the early stages of dementia, individuals often manage their hygiene independently, requiring minimal to occasional assistance. However, as dementia progresses to the middle and late stages, both physical and cognitive decline present challenges to the bathing routine.
Common issues during these later stages include bathing avoidance, a lack of awareness regarding personal hygiene needs, and sensory issues related to bathing or water. Adjusting strategies to support the changing needs and capabilities of dementia patients becomes essential to maintain their autonomy and dignity while ensuring proper hygiene.
Caregivers may need to implement new or unconventional accommodations to facilitate the bathing process for all involved. Understanding the relationship between dementia stages and bathing procedures allows caregivers to provide the highest level of care, promoting hygiene and overall wellbeing.
Caregivers Training On Hygiene Needs
To provide compassionate and effective care, it’s crucial to understand the unique hygiene needs of patients. Caregivers should receive hygiene education that covers the physical and cognitive transitions associated with dementia and how they affect bathtime and personal care routines. This education helps caregivers recognize behaviors and challenges related to grooming and bathing.
By being trained on hygiene needs, caregivers are equipped with essential skills and knowledge to provide support competently while respecting the patient’s individual wishes. This training includes learning practical techniques for bathing and grooming, using strategic communication to address resistance or confusion, and employing methods to increase relaxation and comfort during personal care activities. Ultimately, this training empowers caregivers to deliver high-quality care that meets hygiene needs and enhances the quality of life and well-being of dementia patients.
General Concerns And Inquiries About Showering
It’s crucial for caregivers to understand the concerns that arise around showering in order to offer comprehensive support. The genuine fear of falling and water avoidance are common factors contributing to showering resistance. By creating a safe and supportive environment and addressing individual concerns, caregivers can help individuals with dementia trust the showering process.
Learn What Others Have Experienced with EVY Light
See how others have achieved a sharper mind by activating their gamma brainwaves in combination with maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions About 'why Won't Dementia Patients Take Showers
Why Won't Dementia Patients Take Showers?
How Often Should Dementia Patients Shower?
While regular baths are essential for overall cleanliness and skin health, the frequency of bathing should be tailored to individual circumstances, such as mobility limitations, skin sensitivity, and personal preferences.